Need some additional context? Check out the post: What is Embedded Finance?
Before we can start looking at any term through the lens of Embedded Finance, it's best we first cover the term definition - so let's dive into what exactly Banking as a Service (BaaS) is.
What is Banking as a Service?
It's difficult to pinpoint the exact origin of the term, but it likely emerged as a way to describe a new model of offering banking services to third parties through APIs and other integration methods.
In recent years, APIs have continued to grow in importance and have become a key part of the modern computing landscape. They are used in a wide range of applications and industries, and they have enabled the development of new types of connected services and business models, such as Banking as a Service (BaaS).
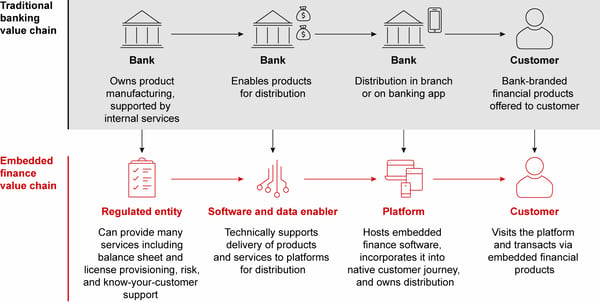
 Banking as a service (BaaS) involves providing financial institutions with the backend infrastructure and capabilities they need to offer financial services to their customers. This can include access to payment processing, account management, and other core banking functions such as card issuance.
Banking as a service (BaaS) involves providing financial institutions with the backend infrastructure and capabilities they need to offer financial services to their customers. This can include access to payment processing, account management, and other core banking functions such as card issuance.
BaaS providers typically charge a fee to financial institutions for access to their platform and services. From the perspective of the financial institution, BaaS can provide a more efficient and cost-effective way of delivering financial services, as it allows them to leverage the infrastructure and expertise of specialized providers.
BaaS has enabled neobanks and challenger banks to enter the market and offer banking services to customers without having to build and maintain their own banking infrastructure. By using BaaS, these banks can access the necessary banking capabilities and resources on demand, allowing them to focus on building and improving their user experience and offering convenient and innovative banking services to their customers.
In recent years, neobanks and challenger banks have gained significant market share and disrupted the traditional banking industry. Many customers have been attracted to these banks due to their digital-first approach and innovative features, such as budgeting tools, rewards programs, and more. Overall, BaaS has played a key role in the growth of neobanks and challenger banks and has helped to drive the evolution of the financial industry - an evolution that has led to Embedded Finance and Cybrid.
How does Embedded Finance differ?
Embedded finance involves integrating financial services directly into the products or services of a non-financial business, providing a front-end experience change for consumers who are used to a more siloed services approach.
For example, a ride-sharing company might offer its drivers access to financing options to help them purchase or maintain their vehicles. This can provide a more seamless and convenient experience for the consumer, as they can access financial services directly within the context of the non-financial business's offering.
Embedded Finance uses the API services and infrastructure that helped create Banking as a Service so the two terms are somewhat intertwined, but a key distinction might be made by looking at the implementation. Banking as a Service focuses primarily on backend innovation for new types of financial companies, where as Embedded Finance focuses more on the front end innovation for new types of financial consumer experiences.
With software and data enabler platforms, like Cybrid, the process of turning an idea into an innovative in-market product is technically simplified and financially viable for companies of all sizes. These platforms provide Infrastructure as a Service, through both APIs and UI SDKs. The UI SDKs reduce the technical burden of embedding the financial product or service by providing building blocks to build from. For example, check our UI SDK codebases.
At Cybrid, we work with a network of regulated entities, partners and vendors to create an Embedded Finance platform that makes available a range of "as a service", such as crypto, that would otherwise not be viable due to financial, technical, legal, or relationship co-ordination related roadblocks.